About Pine Trees
Pine trees are a well-known source of antioxidants and are commonly used in food supplements and phytochemical remedies, such as Pycnogenol, which is also used to help treat chronic inflammation and circulatory dysfunction.
In addition to the traditional use of pine seeds as edible raw nuts or in cooked dishes, pine cones, needles, bark, and oil have long been recognized and accepted as ingredients in both food and skincare around the world. Their benefits include anti-aging properties, protective effects against alcohol-induced liver damage and inflammation, memory-enhancing activity in the hippocampus, and potential support for the early management of dyslipidemia — making them valuable in the food, functional food, and dietary supplement industries.


Yangyang
prounounced yang-yang
Yangyang, known as a place of rest, restoration, and healing, is the eastern coastline region of Korea and home to our Pine Tree Line. Since the old days, Koreans have regarded pine trees as a symbol of life and resilience, which inspired Round Lab to create the Pine Tree Line. It combines Natural Moisturizing Factor (NMF) from pine trees and Madecassoside Extract to promote skin regeneration.
Pine Tree’s Skin Effect Experiment
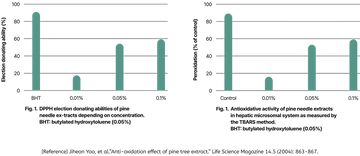
I. Antioxidant effect for anti-aging of skin
The antioxidant effect of the pine needle extract shows increased antioxidadant activities of 18.2%, 64.3%, and 70% at the concentrations of 0.01%, 0.05%, and 0.1%, respectively, indicating that the antioxidant activity significantly increased with increased concentration.
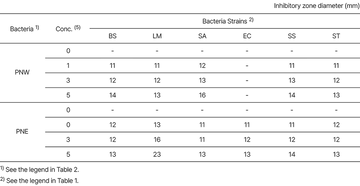
II. Pine Tree’s Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Effect on Skin
The pine needle water extract (PNW) showed strong antibacterial activity against all tested pathogen bacteria strains except for E. coli, and the pine needle ethanol extract (PNE) also showed strong antibacterial activity against all tested bacteria.

III. Pine Tree’s Plant Peptides Effect on Skin
Plant peptides contain amino acids such as glycine, proline, alanine, and hydroxyproline — key building blocks of the body’s major collagen components. Unlike animal-derived collagen, plant-based peptides are more easily and quickly absorbed into the skin.


























